Tile Painting: Revisited!
Nikita just came up with a new array game. The rules are as follows:
- Initially, there is an array, , containing integers.
- In each move, Nikita must partition the array into non-empty parts such that the sum of the elements in the left partition is equal to the sum of the elements in the right partition. If Nikita can make such a move, she gets point; otherwise, the game ends.
- After each successful move, Nikita discards either the left partition or the right partition and continues playing by using the remaining partition as array .
Nikita loves this game and wants your help getting the best score possible. Given , can you find and print the maximum number of points she can score?
Input Format
The first line contains an integer, , denoting the number of test cases. Each test case is described over lines in the following format:
- A line containing a single integer, , denoting the size of array .
- A line of space-separated integers describing the elements in array .
Constraints
Scoring
- for of the test data
- for of the test data
- for of the test data
Output Format
For each test case, print Nikita's maximum possible score on a new line.
Sample Input
3
3
3 3 3
4
2 2 2 2
7
4 1 0 1 1 0 1
Sample Output
0
2
3
Explanation
Test Case 0:
Nikita cannot partition into parts having equal sums. Therefore, her maximum possible score is and we print on a new line.
Test Case 1:
Initially, looks like this:
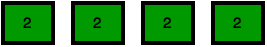

She splits the array into partitions having equal sums, and then discards the left partition:
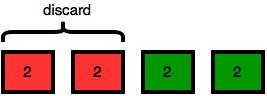
She then splits the new array into partitions having equal sums, and then discards the left partition:
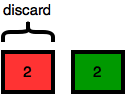
At this point the array only has element and can no longer be partitioned, so the game ends. Because Nikita successfully split the array twice, she gets points and we print on a new line.
------------------------------------------------EDITORIAL------------------------------------------
Solution
This problem can be solved using straightforward dynamic programming. Let's maintain a DP[N][N]table where an entry DP[L][R] denotes the maximum points we can score by playing the game on a subarray from L to R.
We can fill up the DP table in using following recursive recurrence:
- if
- if there is no such .
C++ Code:
Language : C++
Language : C++
const int maxn = 2048 + 10;
int dp[ maxn ][ maxn ], n;
long long int A[ maxn ];
long long int sum(int l, int r) {
return A[r] - A[l-1];
}
int solve(int l, int r) {
int &ret = dp[l][r];
if( ret != -1 ) return ret;
ret = 0;
for(int x=l; x<r; x++) {
if(sum(l, x) == sum(x+1, r)) // valid x
ret = max(ret, max(solve(l, x), solve(x+1, r)) + 1);
}
return ret;
}
int main() {
int t; cin >> t;
while( t-- ) {
int n; cin >> n;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
cin >> A[i];
A[i] += A[i-1];
}
memset(dp, -1, sizeof dp);
cout << solve(1, n) << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
Careful observation reduces the complexity to . It should be noted that maximum points for a subarray can be calculated by considering only the first valid for a subarray (rather than by considering all valid ).
Steps Involved:
- Find first valid for all subarrays.
- Populate DP as shown above but by considering only first valid .
C++ code:
Language : C++
const int maxn = 2048 + 10;
int n;
long long int A[ maxn ];
int L[ maxn ][ maxn ], dp[ maxn ][ maxn ];
int solve(int l, int r) {
if( l > r ) return 0;
if( L[l][r] == -1 ) return 0;
int &ret = dp[l][r];
if( ret != -1 ) return ret;
ret = 0;
ret = max(ret, max(solve(l, L[l][r]), solve(L[l][r]+1, r)) + 1);
return ret;
}
int main() {
int t; cin >> t;
while( t-- ) {
int n; cin >> n;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
cin >> A[i];
A[i] += A[i-1];
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
for(int j=i; j<=n; j++) {
L[i][j] = -1; // to store first valid X
dp[i][j] = -1; // to store maximum points
}
}
// finding first valid X for each subarray
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
long long int s = 0;
int l = i;
for(int j=i; j<=n; j++) {
s += A[j] - A[j-1];
if( s % 2 == 0 ) {
s /= 2;
while( l < j && A[l]-A[i-1] < s) l++;
if( l < j && A[l]-A[i-1] == s ) L[i][j] = l;
s *= 2;
}
}
}
cout << solve(1, n) << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
We can optimize the above solution to work in using binary search. Find the first valid in the range using binary search, then divide the range into parts (i.e.: ), compute the answer for both parts recursively and then take the maximum answer from both parts to compute the answer of range . This can be implemented as follows:
C ++ Code:
long long a[100010];
ll sum(int l, int r) {
return a[r] - a[l-1];
}
// binary search to find first valid X
// within subarray [l, r]
int get(int l, int r, ll s) {
int low, high, mid;
low = l;
high = r;
while( low <= high ) {
mid = ( low + high ) / 2;
ll x = sum(l, mid);
if( x == s && (mid == l || sum(l, mid-1) != s )) {
return mid;
} else if( x >= s ) {
high = mid - 1;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
int solve(int l,int r){
ll s = sum(l, r);
if( l != r && s % 2 == 0 ) {
int ind = get(l, r, s/2);
if( ind != -1 ) {
// compute maximum from 2 parts
return max(solve(l, ind), solve(ind+1, r)) + 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
int t;
cin>>t;
while (t--){
int n;
cin>>n;
assert(n <= 16384);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
cin>>a[i];
a[i]+=a[i-1];
}
cout<<solve(1,n)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}/ MY CODE#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long int lli;
#define ff first
#define ss second
#define mp make_pair
#define pb push_back
int n;
lli arr[162390];
int solve(int l,int r,lli ms)
{
if(l>=r) return 0;
if(r>=n) return 0;
int ci=l;
lli cs=0;
int f=1;
while((cs<ms/2 || f==1) && ci<=r)
{
f=0;
cs+=arr[ci];
ci++;
}
if(cs==ms/2 && ms%2!=1)
{
return max(solve(l,ci-1,ms/2),solve(ci,r,ms/2))+1;
}
else return 0;
}
int main()
{
// freopen("abc.txt","r",stdin);
// freopen("pqr.txt","w",stdout);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
//cout<<"bacl";
scanf("%d",&n);
lli sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%lld",&arr[i]);
sum+=arr[i];
}
if(sum%2==1)
{
cout<<0<<endl;
}
else
cout<<solve(0,n-1,sum)<<endl;
}
}
Problem Setter's code :
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long int
long long a[100010];
ll sum(int l, int r) {
return a[r] - a[l-1];
}
int get(int l, int r, ll s) {
int low, high, mid;
low = l;
high = r;
while( low <= high ) {
mid = ( low + high ) / 2;
ll x = sum(l, mid);
if( x == s && (mid == l || sum(l, mid-1) != s )) {
return mid;
} else if( x >= s ) {
high = mid - 1;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
int solve(int l,int r){
ll s = sum(l, r);
if( l != r && s % 2 == 0 ) {
int ind = get(l, r, s/2);
if( ind != -1 ) {
return max(solve(l, ind), solve(ind+1, r)) + 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
int t;
cin>>t;
while (t--){
int n;
cin>>n;
assert(n <= 16384);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
cin>>a[i];
a[i]+=a[i-1];
}
cout<<solve(1,n)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
Problem Tester's code :
//O(N*ANS)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long a[1000000];
int sol(int l,int r){
for (int x=l;x<r;x++)
if (a[x]*2==a[r]+a[l-1]) return max(sol(l,x),sol(x+1,r))+1;
return 0;
}
int main() {
int t;
cin>>t;
assert(t<=10);
while (t--){
int n;
cin>>n;
assert(n<=16384);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
cin>>a[i];
assert(a[i]<=1000000000ll);
a[i]+=a[i-1];
}
cout<<sol(1,n)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}